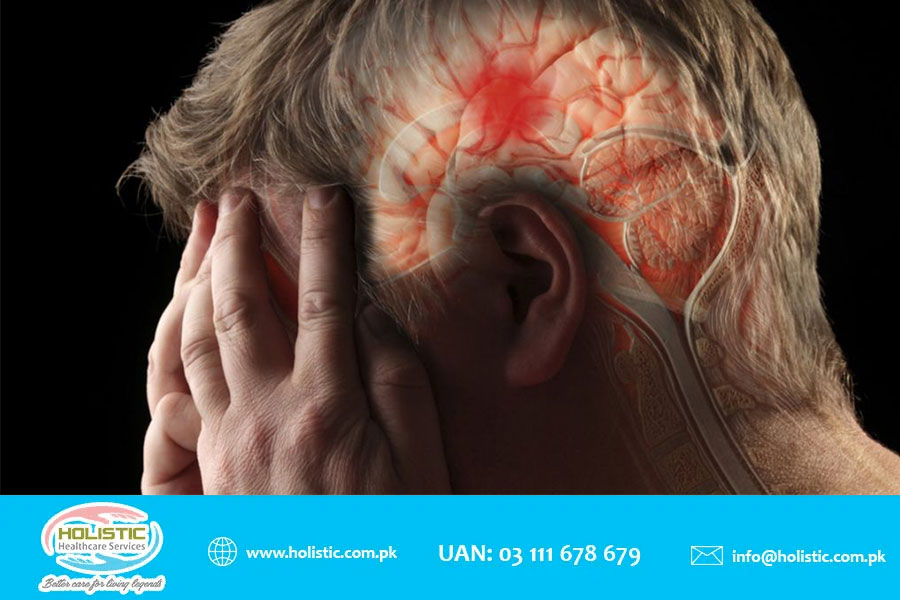
A stroke is a sudden interruption in the blood supply of the brain. Most strokes are caused by an abrupt blockage of arteries leading to the brain, which is usually referred to as an ischemic stroke. Stroke is a disease that affects the arteries leading to and within the brain. It is the No. 5 cause of death and a leading cause of disability in the United States. It usually occurs when a blood vessel that carries oxygen and nutrients to the brain is either blocked by a clot or bursts or ruptures.
Symptoms of Stroke
Symptoms vary depending upon the area of the brain affected by a lack of oxygen. All strokes involve symptoms that relate to impairment of nerve function. These symptoms typically arise suddenly and most commonly occur on one side of the body. Symptoms and signs can include:
1) Numbness
2) Weakness
3) Tingling or
4) Vision loss or changes
Confusion and changes in the level of consciousness, trouble speaking, trouble understanding speech, vertigo, and balance problems are other common symptoms. Headache, nausea, and vomiting are also common symptoms, particularly when the condition involves bleeding inside the brain.
Types
A stroke is also called a cerebrovascular accident, CVA, or “brain attack” and includes the following types:
1) Ischemic stroke (part of the brain loses blood flow)
2) Hemorrhagic stroke (bleeding occurs within the brain)
3) Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) or mini-stroke
Usually, symptoms resolve within minutes but may take up to 24 hours to subside on their own without treatment. This is a warning sign that a stroke may occur in the near future.
Causes
There are a number of reasons for an artery in the brain being obstructed or blocked, preventing oxygen-rich blood from being delivered to the brain cells. The artery can be blocked in a couple of ways. In a thrombotic stroke, an artery can narrow over time because of cholesterol build-up, called plaque. If that plaque ruptures, a clot is formed at the site and prevents blood from passing to brain cells downstream, which are then deprived of oxygen.
In the case of hemorrhagic stroke, bleeding or hemorrhage suddenly interferes with the brain’s function. This bleeding can occur within the brain or between the brain and the skull. Hemorrhagic strokes account for about 20% of all such cases and are divided into categories depending on the site and cause of the bleeding.
Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA), also known as a mini-stroke, has stroke-like symptoms. It usually lasts less than one hour. A TIA is an emergency which means that the patient can suffer from a stroke within the next 24 hours. A patient whose blood pressure’s lower reading is high is more prone to TIA than a patient with normal readings.
Treatment
From the onset of symptoms, there is only a 3 to 4 1/2 hour window to use clot-busting drugs (thrombolytics) to try to restore blood supply to the affected part of the brain.
Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA or PLAT) is an emergency medication that can be used to break up a blood clot causing the stroke.
Anticoagulants are drugs that reduce your blood’s ability to clot. They are used in stroke patients, along with Antiplatelet drugs, Statins, and other Blood pressure drugs.
If you have a stroke patient at home who needs care, we can be of assistance. Holistic Healthcare Services has been providing healthcare services to patients and elderly people in the comfort of their homes. We have qualified and experienced nurses, caregivers, and attendants who can assist patients at their homes. Call us today at 03 111 678 679 to know more about our services.


 Reach us on WhatsApp
Reach us on WhatsApp